| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE | |
| PUMP STORAGE SYSTEMS | |
| V. Ryan © 2005 - 2017 | |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET | |
| CLICK HERE FOR POWERPOINT VERSION OF WORKSHEET | |
|
The principle behind pump water storage systems is
very simple. Electricity costs more to produce during the day time
because it is in greater demand by customers and businesses (called peak
time). At night time electricity is cheaper, this is called 'off peak'
time, as less people and businesses need large amounts during the night.
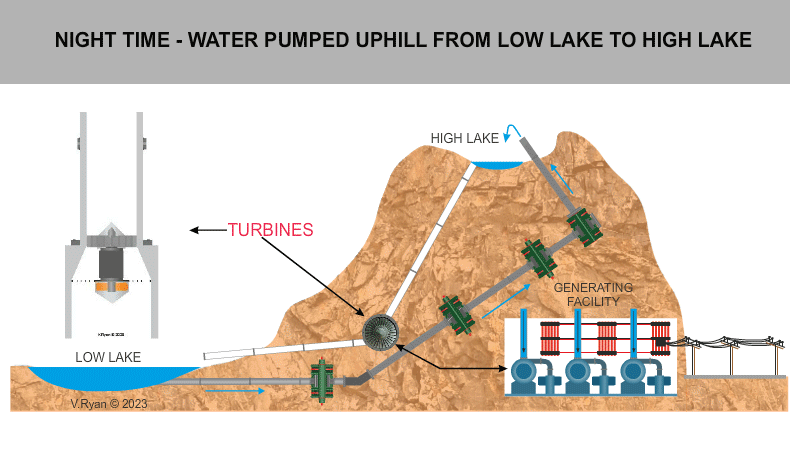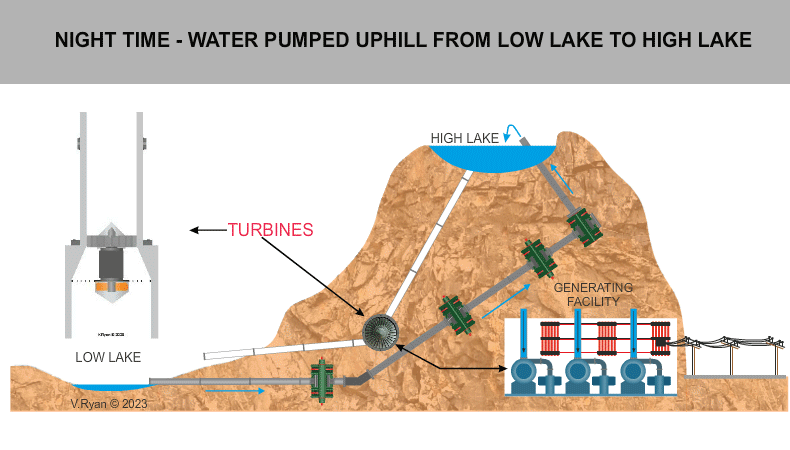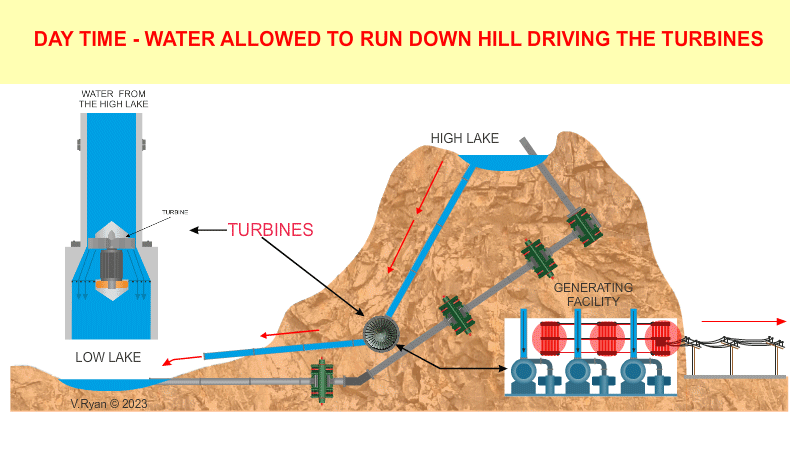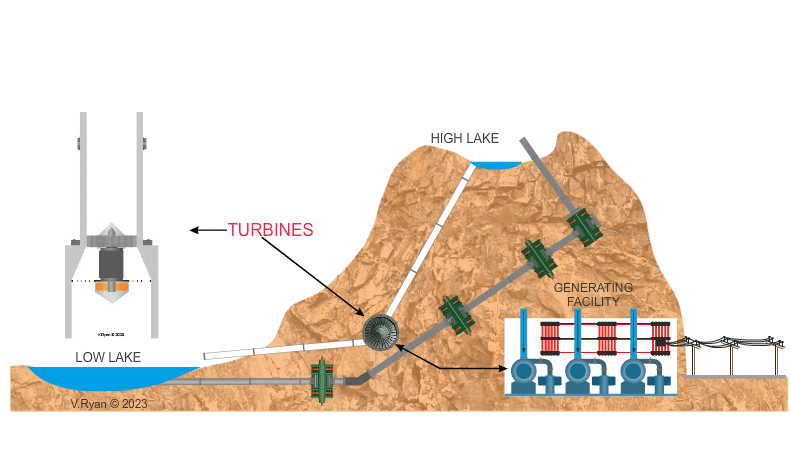
During the night, water is pumped from a
low lake to a high lake. Cheap electricity is used to carry out this
process. During the day time the water from the high lake is released in
a controlled way and as it descends at high speed, it is used to turn
turbines, generating electricity. |
|
 |
|
|
The system is mainly housed within man-made caverns inside the mountain and so impact on the environment is minimal. Natural lakes at the top and bottom of the mountain are used as the low and high lakes. The system is generally used to support the National Power Grid at peak times, when demand for electricity is at its greatest. Water is released from the high lake when electricity is needed. At night time the water in the low lake is pumped back up the mountain to the high lake, for use again. |
|
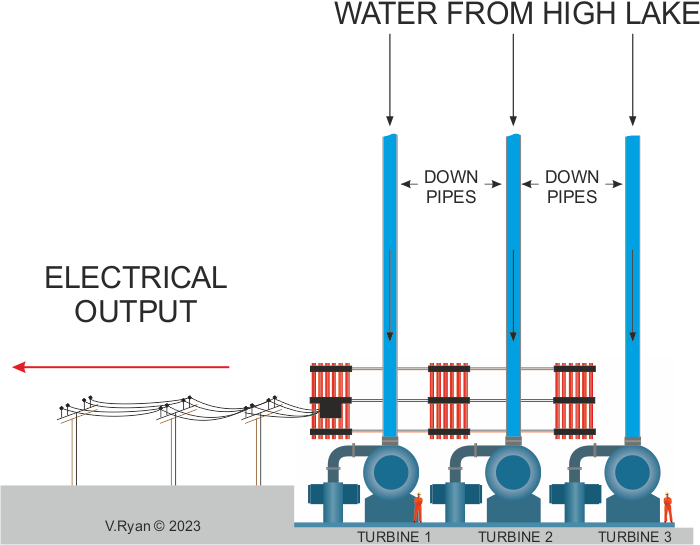
| THE TURBINE HALL | |
| The high lake supplies water through a number of ‘down pipes’, feeding the turbines. The turbines convert the downward flow of the water to electricity electricity. | |
 |
|
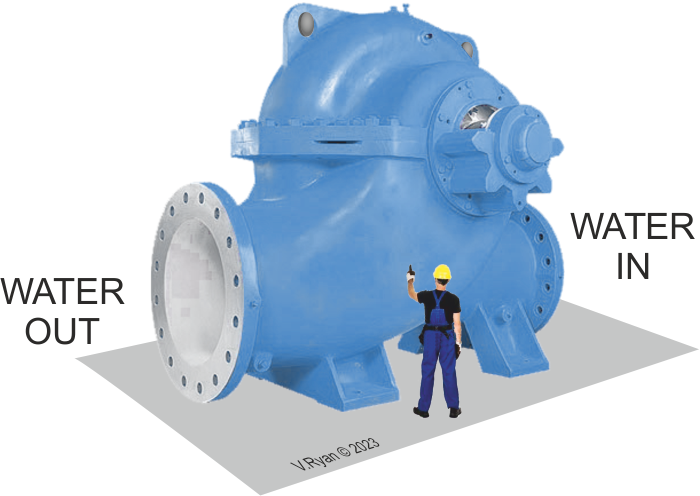
| COMPARATIVE SIZE OF EACH TURBINE | |
| Each turbine is enormous, as seen in the image below. A turbine is composed blades arranged in a circle. When the water flows through the turbine the blades spin at high speed, causing a rotor generator to produce electricity. | |
 |
|
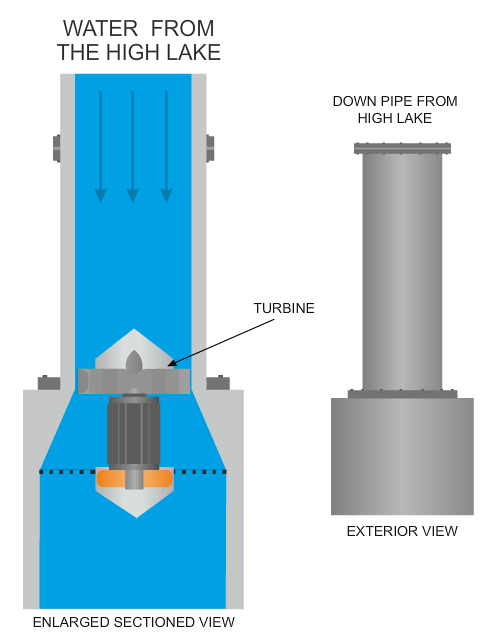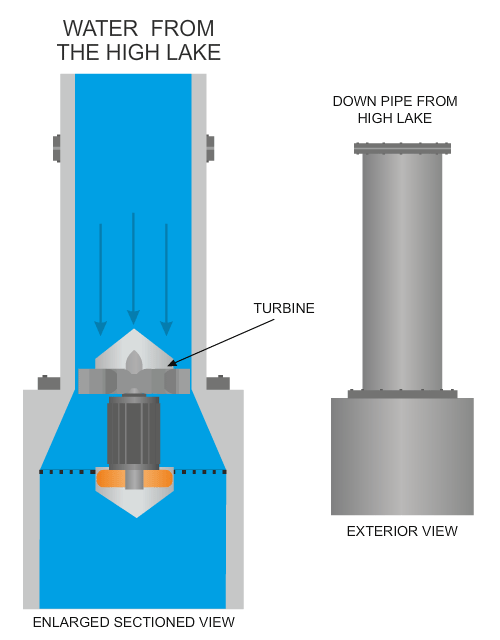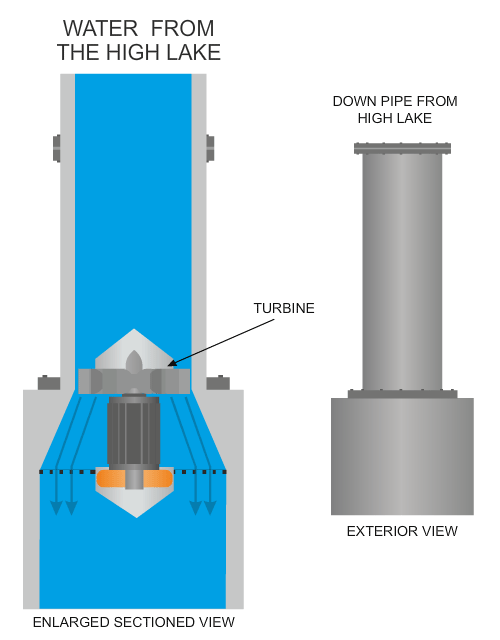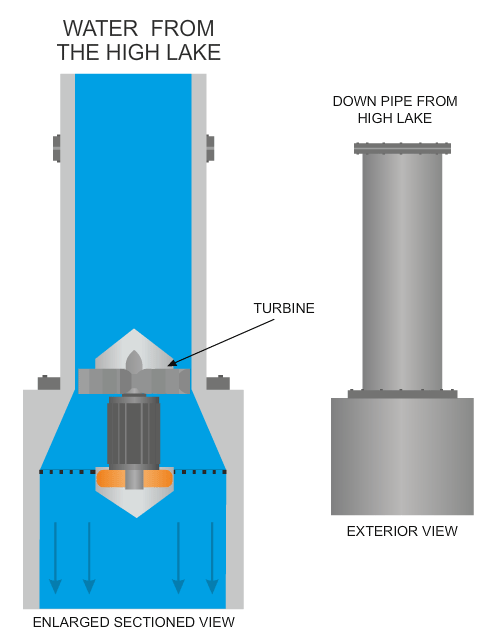
| The diagram below shows a typical turbine, with its turbine blades being forced round by the force of water, generating electricity. | |
 |
|
| CLICK HERE FOR TECHNOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT INDEX PAGE | |
|
|
|