| |
| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE |
| |
THE STORAGE / DISPOSAL OF RADIOACTIVE WASTE
PRODUCED BY NUCLEAR POWER STATIONS |
| V. Ryan © 2006 - 2009 |
| |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET |
| |
| The production of wastes by nuclear power, its
storage and handling are of great concern to the public. There are three
levels of nuclear waste, low activity or low level, intermediate
activity or intermediate level and high activity or high level wastes. |
| |
| LOW LEVEL WASTE |
| |
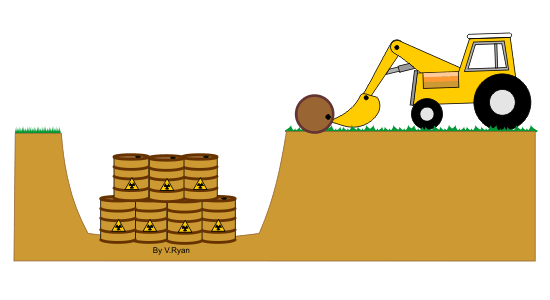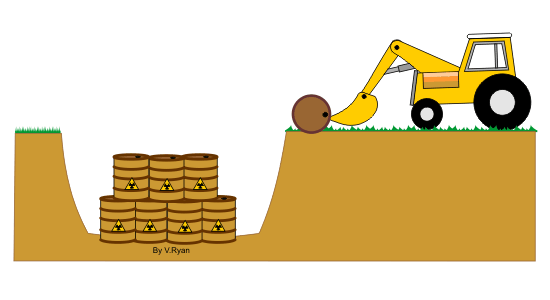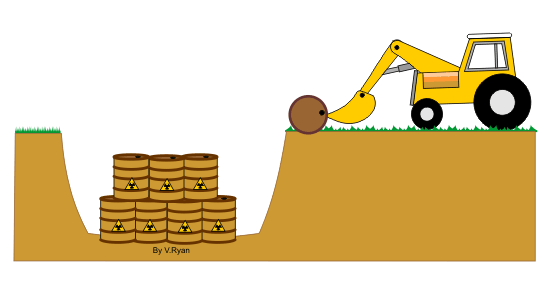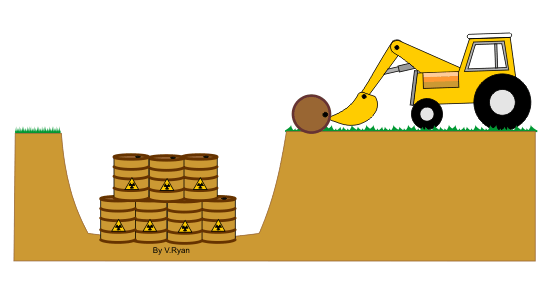
Low level waste include materials that are used to
handle nuclear material such as radiation suits and laboratory
equipment. They are normally stored for up to 15 years in secure storage
and then, after careful packaging they can be disposed of as normal
waste.
However, there is disagreement over the way the waste is disposed. For
example, The British and Irish Governments do not agree on the disposal
of low level radioactive material in the Irish Sea. |
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
| INTERMEDIATE LEVEL WASTE |
| |
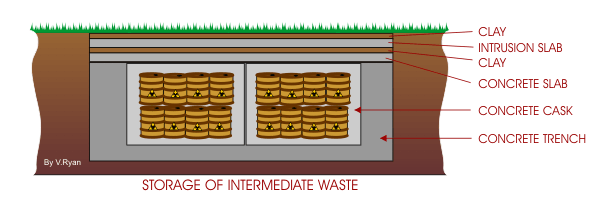
These are much bulkier materials and are
characterised by low heat emission. They contain metal fuel cladding,
chemical sludges and other radioactive wastes.
The waste is first encased in resin or concrete and sealed in steel
drums. The drums are then packed into concrete casks and placed in
concrete trenches up to 18 metres deep. When completely filled the
trenches are covered with a concrete slab, a layer of compacted clay and
a reinforced concrete intrusion shield and a final layer of clay. Deep
disposal of intermediate wastes also takes place, storing the wastes in
a suitable geological formation at a depth of at least 100 metres |
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
| HIGH LEVEL WASTE |
| |
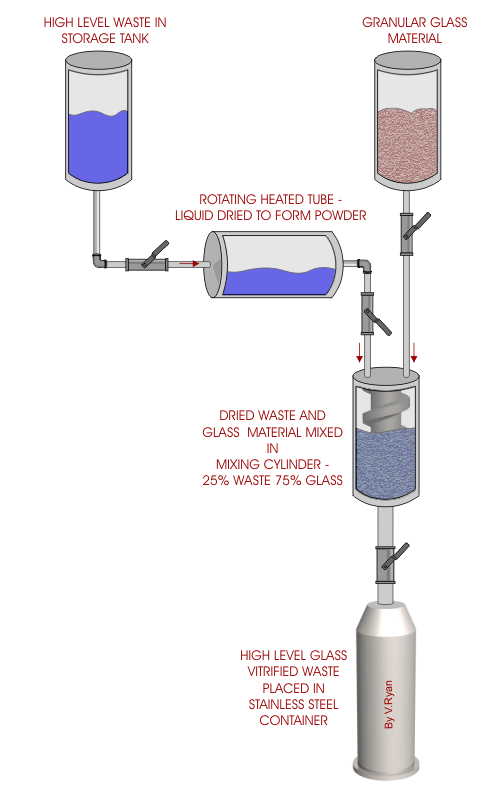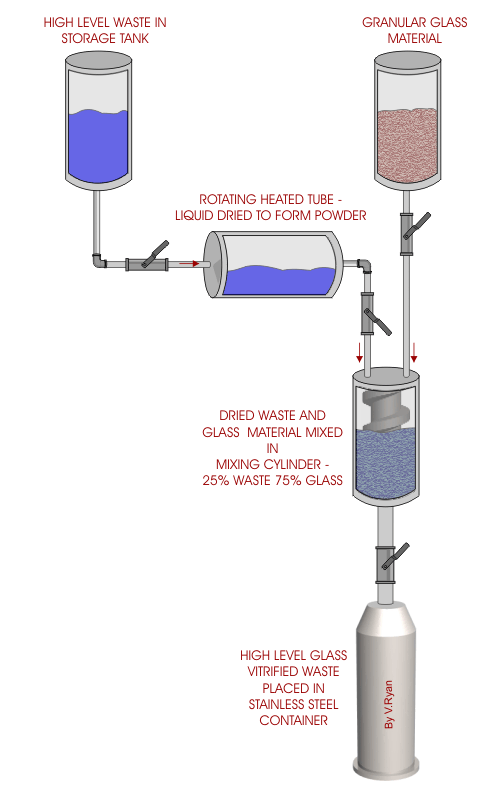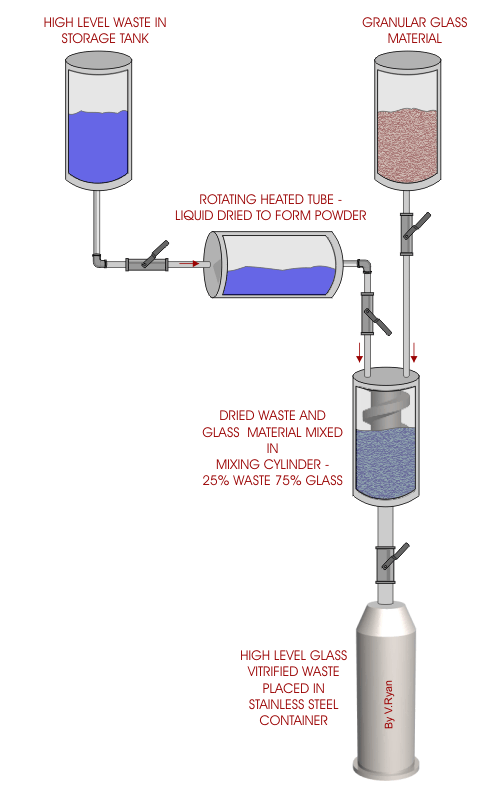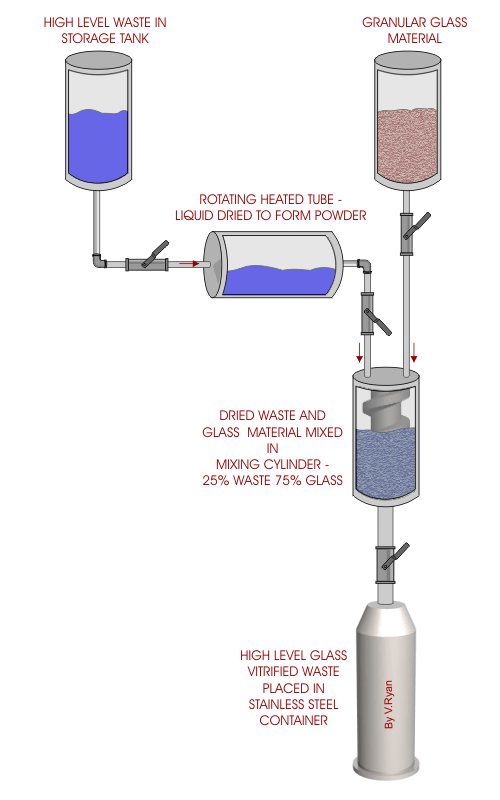
| High level waste is extremely radioactive and remains
in this state for thousands of years. Safe and stable storage of this
type of waste is of great concern. Modern storage methods include the
use of glass vitrification. This involves combining the radioactive
liquid waste with glass to form a solid compound. Because of the solid
nature of the waste it is much less likely to contaminate the
surrounding area. Unlike liquid waste, it cannot leak into the ground if
the stainless steel container it is in becomes faulty. In theory, the
highly radioactive waste can be stored indefinitely in deep stable
formations such as caves and caverns. |
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
QUESTIONS:
1. In you opinion, do you think producing electricity through nuclear power
is safe?
2. Can countries that rely on oil,
coal and gas to produce electricity ignore the need to develop nuclear
power stations? Remember to consider - the green house effect, global
warming, pollution and world politics when answering this question. |
| |
| CLICK HERE FOR TECHNOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT INDEX PAGE |
| |


