| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE |
| THE BLAST FURNACE - IRON PRODUCTION |
| V. Ryan © 2011 - 2021 |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET |
| PowerPoint Version - CLICK HERE FOR WORKSHEET |
|
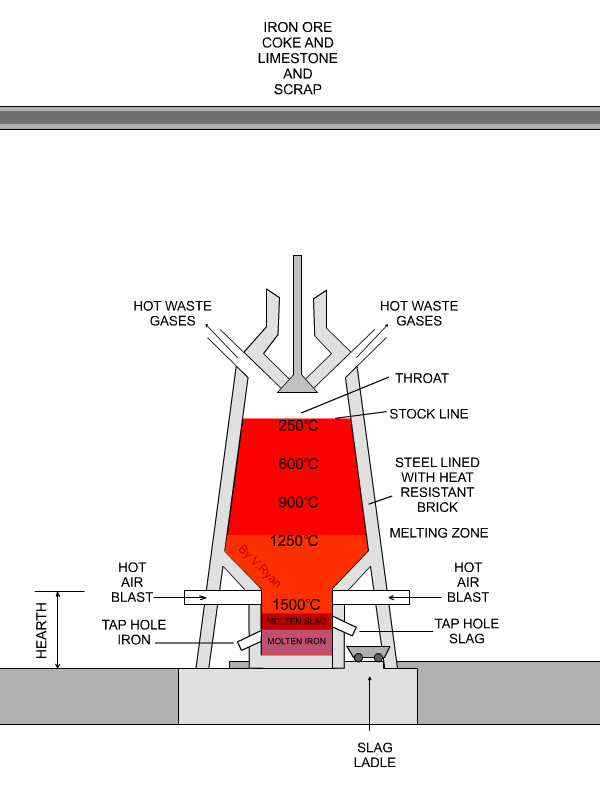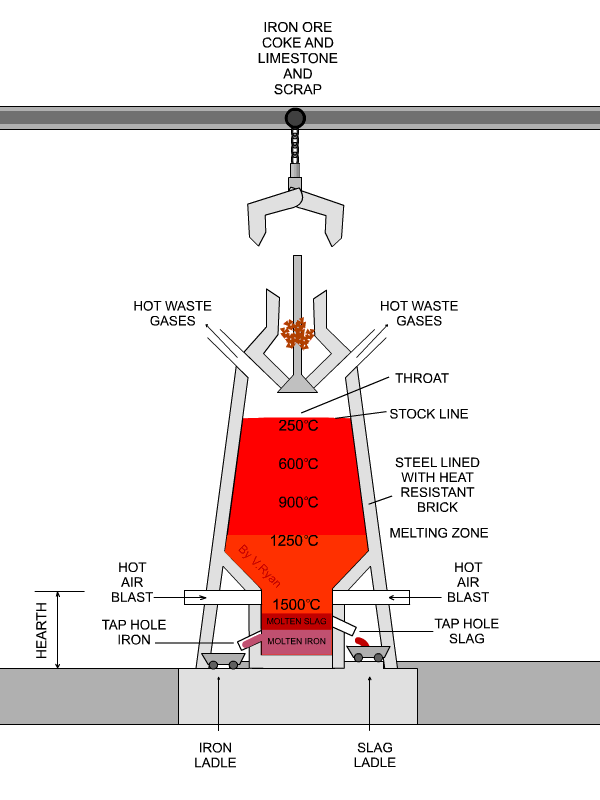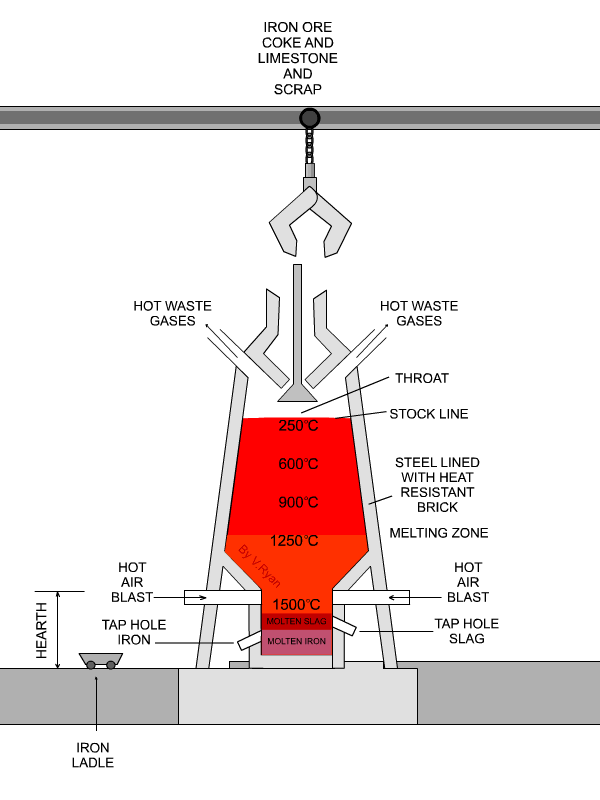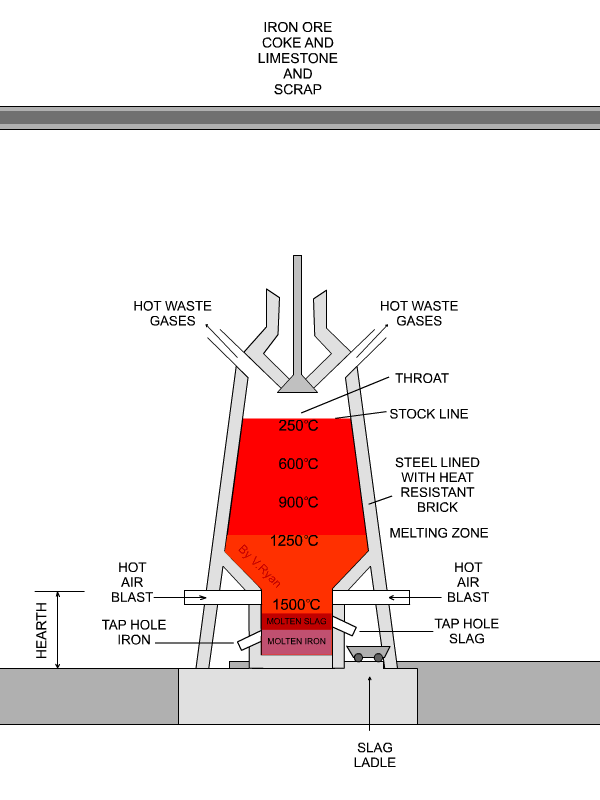
A simplified diagram of a Blast Furnace is drawn below.
A typical blast furnace may be up to 32 metres in height and 10 metres in
diameter. They have thick steel sides, lined with refractory bricks, to
ensure that heat is not lost. Blast furnaces are used continuously and are
only shut down when their brick lining needs replacing. |
| The stock level is constantly ‘topped up’. Molten iron ore is ‘tapped’ at the bottom of the blast furnace, poured into the iron ladle and removed for use. |
| The slag is removed at the tap hole. Although generally regarded as waste, it is used in road making. |
 |
| CLICK HERE FOR RESISTANT MATERIALS INDEX PAGE |