V.Ryan © 2018-2021
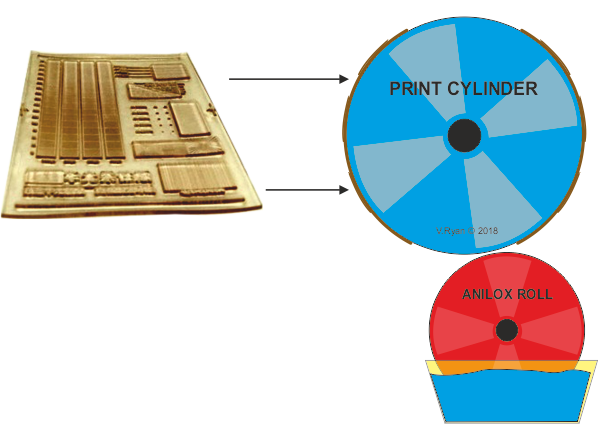
Flexographic printing (also known as Flexo), results in a clearly printed image,with sharp colour quality. This makes the flexo printing process popular with the packaging industry and many others. Improvements to this process are relatively recent and is due to print plates being made to greater precision, through the introduction of computer control and 3D systems. The flexographic process is the modern, technological version, of the letter press.
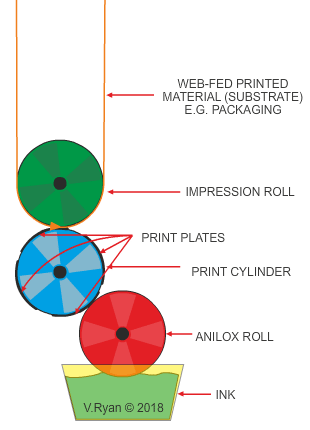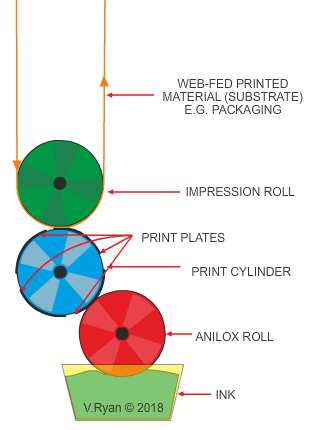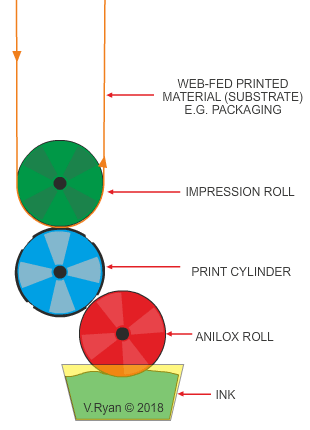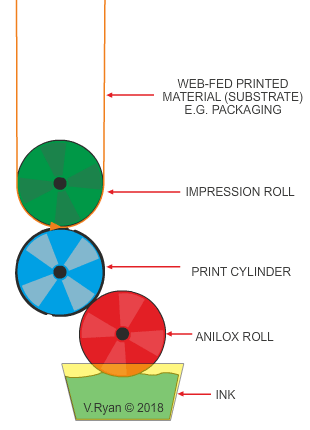
The manufacture of the ‘flexible’ print plates is costly, making this printing process economiwith large continuous print runs only. Flexographic printing is usually combined with web-fed systems (the material to be printed on, is supplied in large rolls). The inks are in the form of gels (not liquids) and therefore, fast drying.
The process is ideal for the printing of packaging, wallpaper, calendars, books, laminated tetra paks and food packaging. The material that receives the print, known as the substrate, can be paper, card, polymers, textiles and even metallised films (polymers coated with a thin layer of metal).

Advantages:
Only economic on long print runs.
Fast and simple, with minimal breakdowns, ensuring continuous print runs. Low maintenance costs.
Can be combined with web-fed systems (rolls of substrate), which is much cheaper and faster, than using a sheet fed system.
Often combined with die cutting and laminating, as one machine.
Fast drying inks (even bio-inks) can be used. Some inks can even infuse wax coatings as found with tetra paks, OR dry as a separate coat, on the surface of tetra paks.
Disadvantages:
Modern print plates suitable for flexographic printing, are extremely expensive and are not economic for short print runs.
Changing from one print run, to a completely different print run, is time consuming and therefore costly.
The printing machinery can only be operated by trained, semi skilled staff.
Interruptions to a print run can be costly.