| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE | |
| INCANDESCENT LAMPS (BULBS) - 1 | |
| V. Ryan © 2005 - 2022 | |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE EXERCISE BASED ON WORK BELOW | |
| Bulbs have been used in electronics for along time and they are used in a wide range of circuits. Almost everyone has used a torch and if you look closely at the light source, it is more than likely that it is a bulb. In more recent years bulbs have been slowly replaced by LEDs as these are brighter, much more reliable, cheaper, energy efficient and have a much longer working life. They are also available in a range of colours. However, bulbs are still popular. | |
|
|
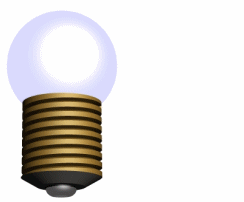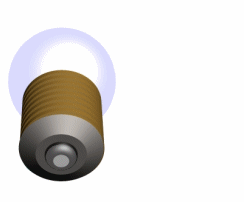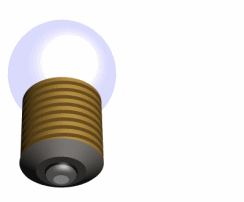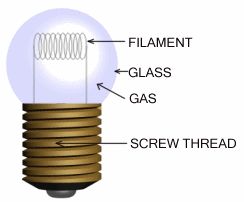
Look closely at a typical torch bulb. It basically
consists of glass ‘bulb’, inside which is a filament made from a metal
called tungsten. The glass bulb holds a gas called Argon or Nitrogen or
Krypton, which increases the working life of the filament. |
|
|
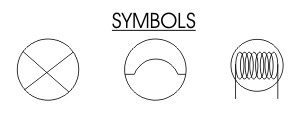
A number of symbols can be used to represent a bulb. Three typical symbols are shown opposite. These are often seen in examinations and consequently it is important to know them. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
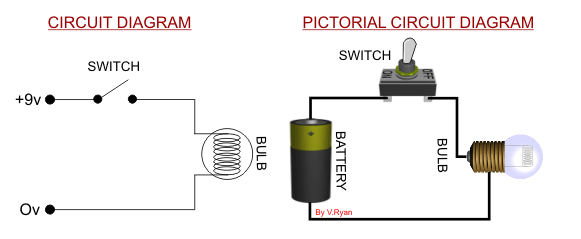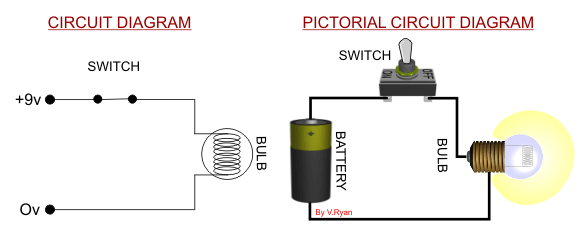
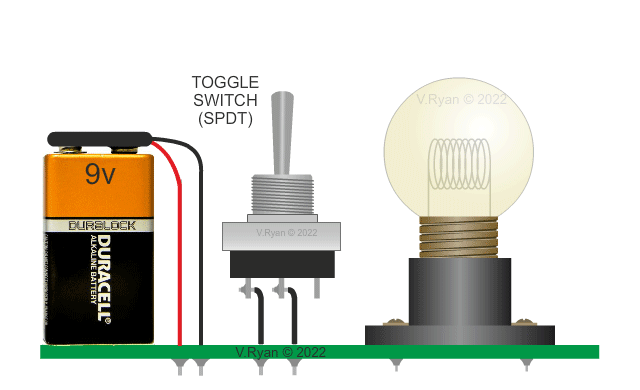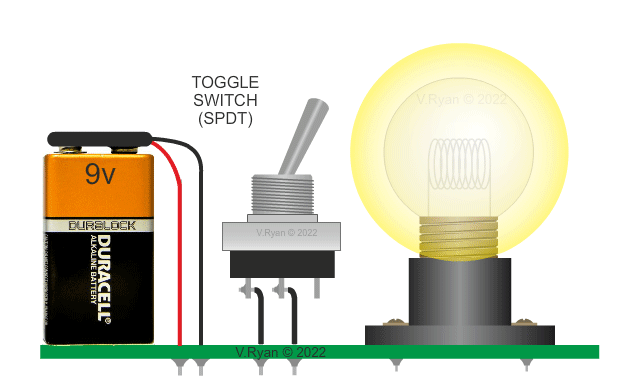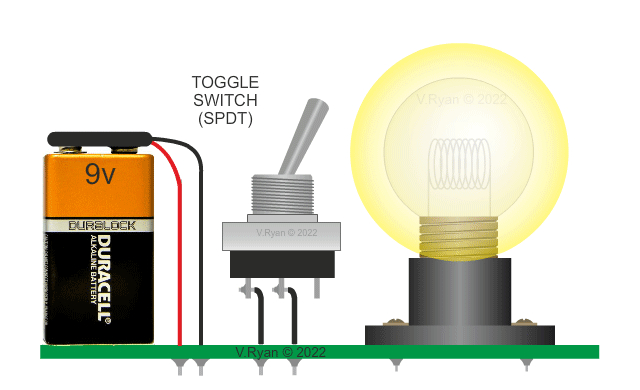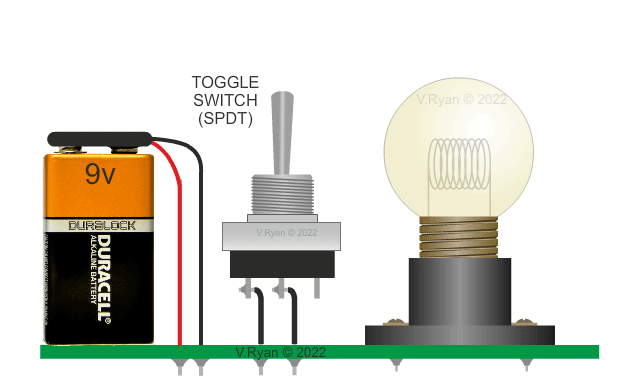
Two versions of the same circuit are shown below. The
conventional circuit diagram (on the left) shows the filament bulb
lighting brightly when the switch is turned on. The current flows
through the filament, causing light to be emitted. |
|
|
|
|
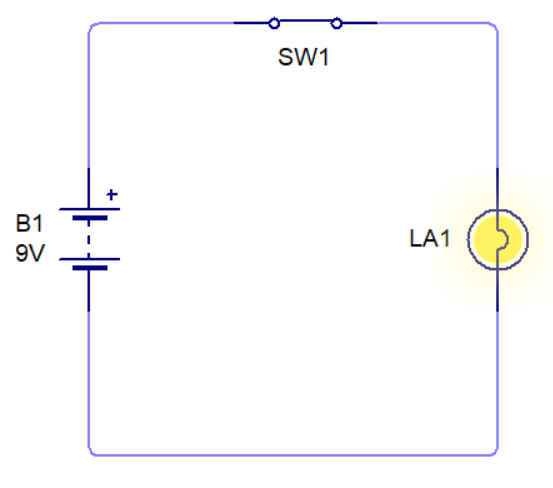
This basic circuit has a battery as the electrical ‘source’ and a filament bulb. The bulb is called the ‘load’ as it does all the work in the circuit (ie. it lights). Circuit Wizard software is very useful when simulating this type of circuit diagram (see below). |
|
|
|
PICTORIAL REPRESENTATION OF THE 'BULB' CIRCUIT |
|
|
|
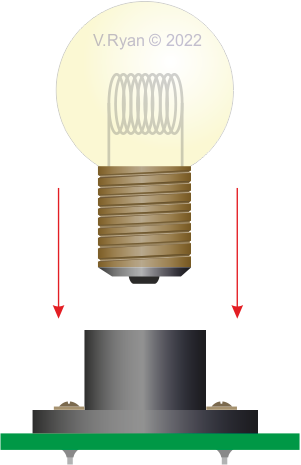
| Bulbs tend to have a screw thread. The bulb is tightened in the bulb holder, which has already been soldered to the PCB (Printed Circuit Board). | |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|