| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE | ||
| REVISION CARDS - SOLDERING | ||
| V. Ryan © 2013-2022 | ||
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET | ||
|
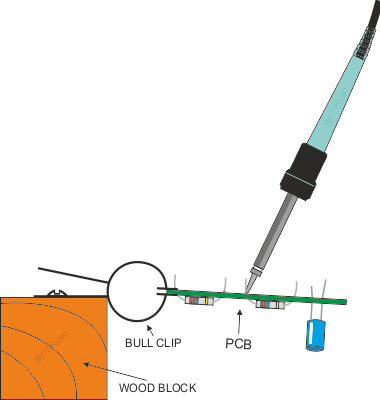
BASIC SOLDERING 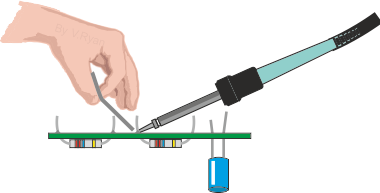 Stage one: Clean the track side of the PCB with wire wool or a PCB eraser. Stage two: Position the components, checking they are in the right position and the correct way round. Stage three: Clean the tip of the ‘hot’ soldering iron, by wiping it on a damp foam pad. Stage four: Heat both the component and the copper track and then apply the solder. |
WHAT IS SOLDER? Electronic components are metallurgically joined to the copper tracks of a PCB, using solder. Solder is an alloy of tin and lead (63% tin and 37% lead). Lead is toxic. Consequently, lead free solder is popular. The lead has been removed and replaced with other metals. However, these solders work at higher temperatures. |
|
|
GOOD AND BAD JOINTS Good soldering produces a ‘concave’ solder joint. The soldering iron must be at the right temperature, applied to the track and ‘wire’ for the right amount of time, with a ‘small’ amount of solder applied. 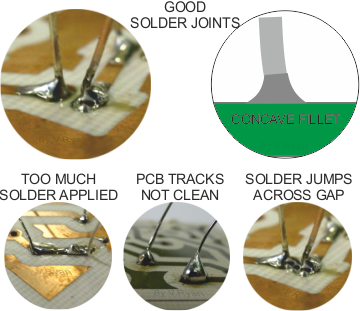 |
 |
|
| QUESTIONS | ||
| 1. Describe soldering components to a PCB , in four simple stages. 4 marks | ||
| 2. What is solder? Why is lead free solder popular? 3 marks | ||
| CLICK HERE FOR PCB INDEX PAGE INDEX PAGE | ||