| |
| CLICK HERE FOR INDEX PAGE |
| |
| WHAT IS PHOTOVOLTAICS ? |
| V. Ryan © 2005 - 2023 |
| |
| PDF FILE - CLICK HERE FOR PRINTABLE WORKSHEET |
| |
| CLICK HERE FOR POWERPOINT VERSION OF WORKSHEET |
| |
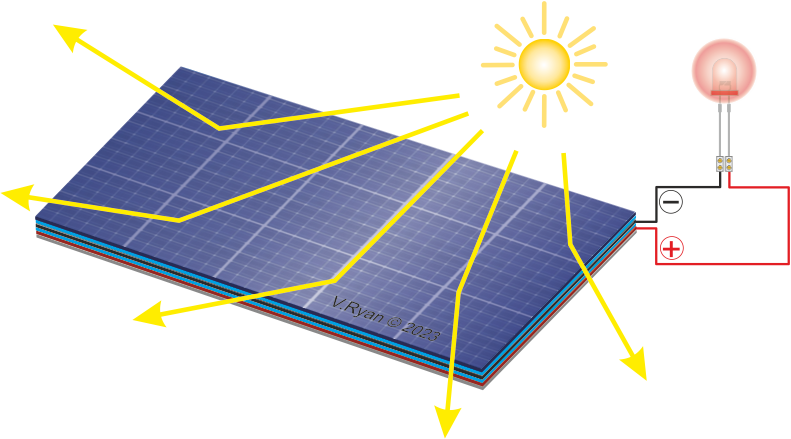
Photovoltaic cells look similar to solar panels but
they work in a different way. Solar panels are use to produce hot water
or even steam. Photovoltaic panels convert the sunlight directly into
electricity. A typical example of a device powered by photovoltaic cells
is a solar powered calculator. This type of device only needs a small
amount of electrical power to work and can even be used in a room with
artificial light (bulbs / fluorescent light).
Although we see photovoltaic cells powering small devices such as
calculators they have a more practical application especially in the
third world. Photovoltaic cells have been developed that will provide
electrical power to pump drinking water from wells in remote villages.
British Telecom have developed a system that can be used to power a
radio telephone system. During the day the cells power the phone and
also charge batteries. The batteries power the phone during the night.
Often photovoltaic cells are used as a backup to conventional energy. If
conventional fails the cells are used to produce electricity. |
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
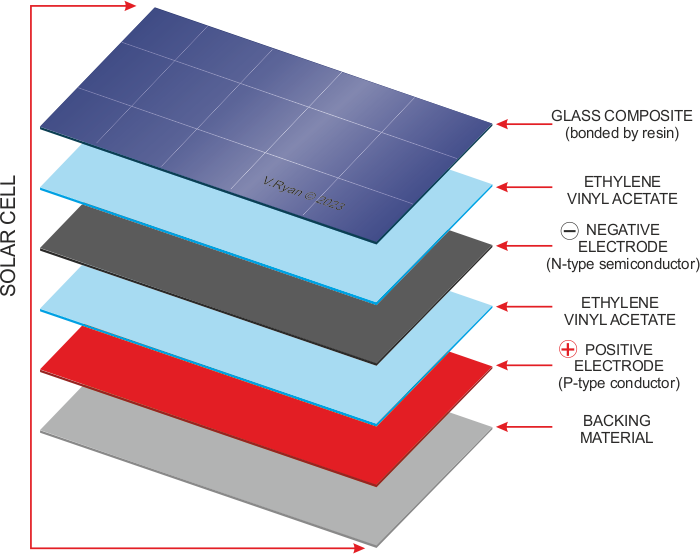
| COMPOSITION OF A PHOTOVOLTAIC PANEL |
| |
| Photovoltaic cells are composed of a number of layers (see below) |
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
| A TYPICAL PHOTOVOLTAIC CELL |
| |
| Silicon is a material known as a ‘semiconductor’ as
it conducts electricity and it is the main material for photovoltaic
cells. Impurities such as boron or phosphorus are added to this base
material. These impurities create the environment for electrons to be
freed when sunlight hits the photovoltaic panel. The freeing of
electrons leads to the production of electricity. |
| |
 |
| |
| The diagram above shows a basic photovoltaic cell.
The blue represents the main material, silicon. The black round and
irregular shapes represent the impurities of boron or phosphorous. As
the sun/light strikes the cell the impurities free up electrons which
‘bounce’ around at incredible speeds. This creates an electrical charge. |
| |
|
|
| |
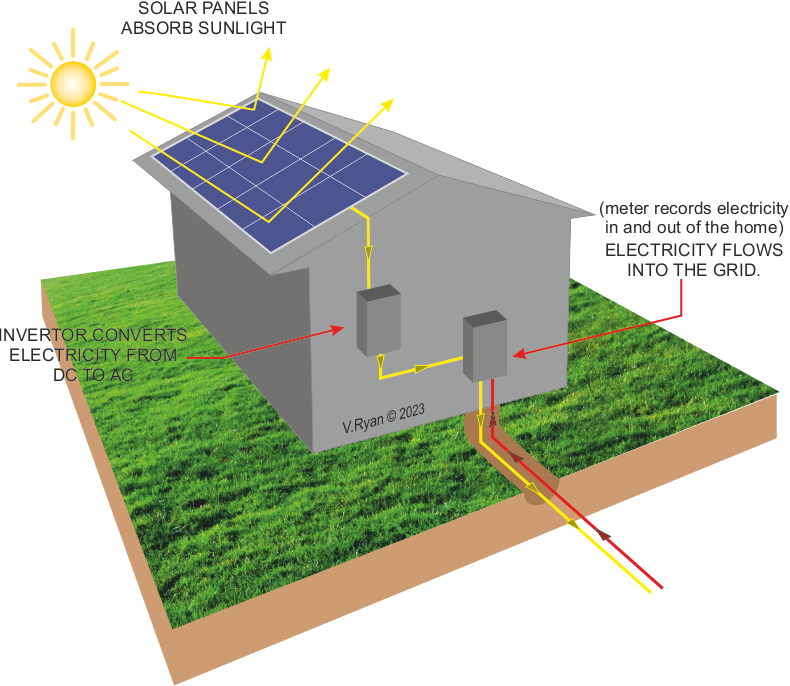
Solar panels on a roof, are usually fixed permanently in one optimum position. A
typical home with solar panels consumes electricity produced by the solar panels. If more, electricity is required, it is ‘imported’ from the National Grid. If more than is need is produced, excess electricity is exported to the national grid. An smart electric meter records electricity production form the solar panels, usage in the home, and import / export of electricity to and from the grid. |
| |
 |
| |
 |
| |
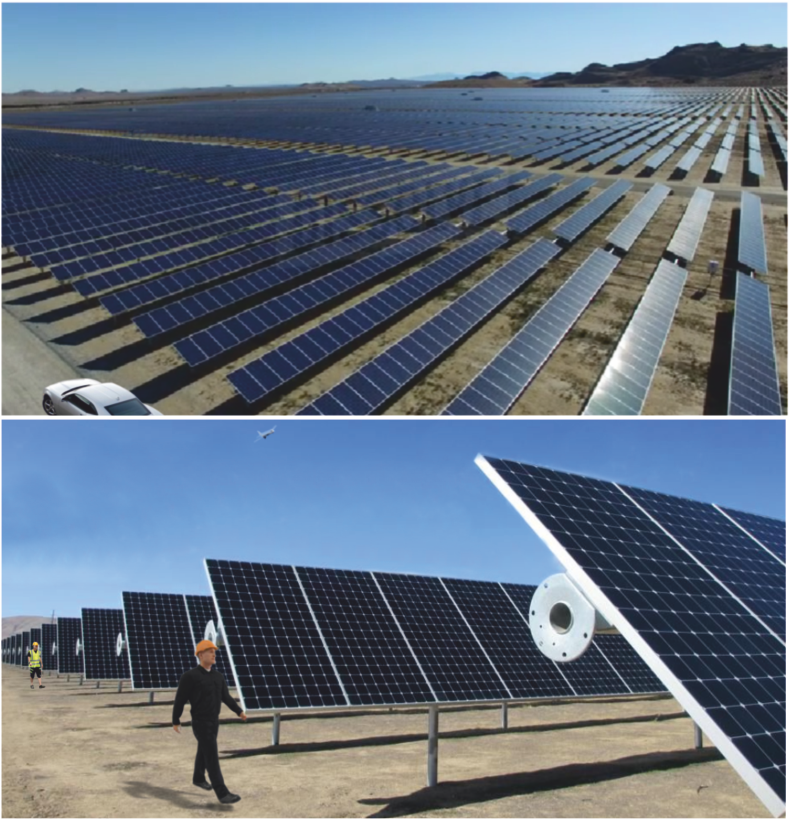
| AN ARRANGEMENT OF PHOTOVOLTAIC PANELS - ARIZONA
(USA) |
| |
 |
| |
|
|
| |
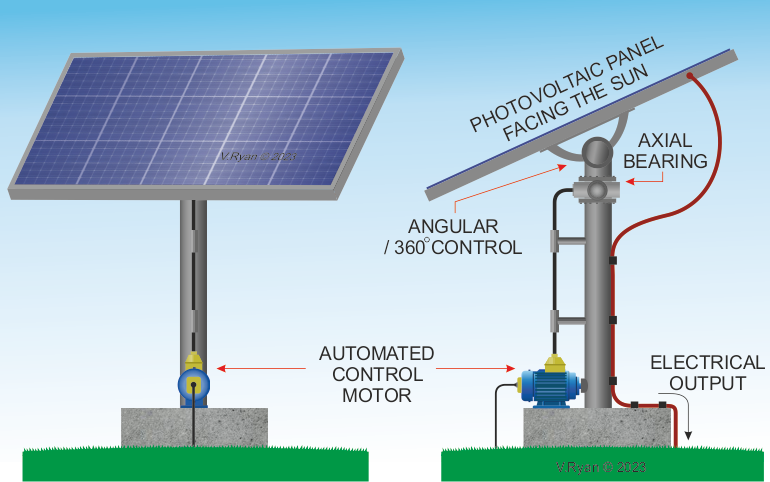
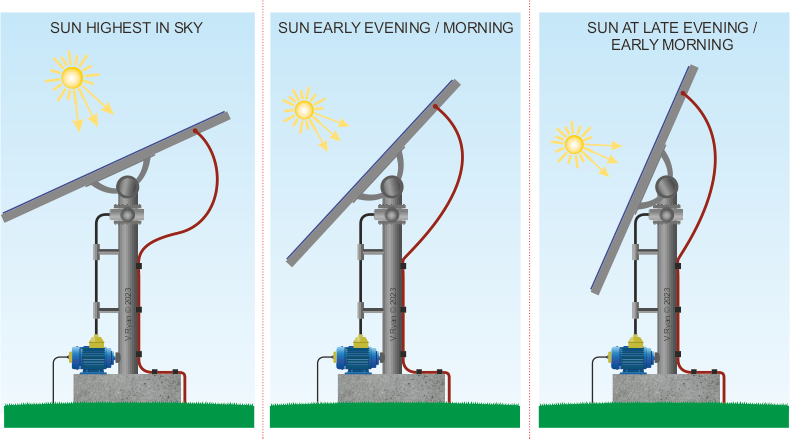
| HOW PHOTOVOLTAIC PANELS ARE AUTOMATICALLY POSITIONED TO TAKE ADVANTAGE OF THE SUN |
| |
The photovoltaic solar panel follows the sun, driven by a precise motor. This is an automated process, with the angle of the panel and the degree of horizontal rotation being controlled by a computer. This ensures that the panel always faces the sun and operates at its most efficient. The amount of energy needed to control the direction and angle of the panel, is small compared to the amount of electricity produced.
The photovoltaic panels are washed regularly, to remove dirt and debris. If dirt and dust was allowed to collect on the panels surface, the amount of electricity generated would be reduced. |
| |
 |
| |
AUTOMATED SYSTEM - ALTERS SOLAR PANEL ANGLE AND 360 SETTING
ACCORDING TO THE TIME OF THE DAY / POSITION OF THE SUN |
| |
 |
| |
QUESTIONS:
1. Make a list of devices that are
powered by photovoltaic cells.
2. Describe devices that you think
could be powered by photovoltaic cells (fully powered or as a backup to
the electricity power grid). |
| |
| CLICK HERE FOR TECHNOLOGY AND ENVIRONMENT INDEX PAGE |
| |
| |
| |







